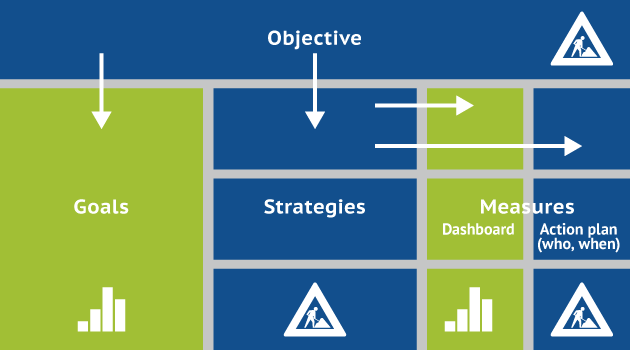
The OGSM framework is a strategic planning tool that aligns an organization’s mission and vision with actionable business strategies and measurable outcomes. Standing for Objectives, Goals, Strategies, and Measures helps companies and teams state what they aspire to achieve in the long term and identify and track the progress of specific goals.
It’s a model that bridges the gap between conceptual planning and practical implementation, fostering clear communication and focused direction within a business.
Translating a business vision into tangible success requires a structured approach, which is where the OGSM model excels. It starts by setting broad objectives that capture the essence of a company’s vision.
Goals then break down these broad objectives into more specific targets achievable within a certain timeframe, often fostering a sense of direction and urgency.
Strategies outline the methods or pathways the organization will employ to reach these goals, and measures provide the metrics used to assess these strategies’ effectiveness continuously.
Utilizing the OGSM Model can be particularly beneficial in ensuring daily operations align with the company’s strategic vision.
This model not only aids in clarifying and communicating a company’s strategic direction but also allows for the regular tracking of performance, ensuring that each department’s efforts contribute effectively to the overarching business goals.
The clear structuring of objectives, strategies, and measures facilitates adaptability and responsiveness within an evolving business environment.
Understanding OGSM
The OGSM Framework is a strategic planning tool that enables organizations to link their long-term visions to actionable strategies. It is abbreviated as OGSM and stands for Objective, Goals, Strategies, and Measures. This model provides a clear structure to ensure that every part of the organization aligns with the overall vision.
- Objective
The Objective is a clear, concise statement encapsulating the organization’s goals. It is the foundation of the OGSM model and sets a broad yet focused direction.
- Goals
Goals are specific targets that are designed to be measurable and time-bound. They break down the Objective into smaller, achievable outcomes, allowing for monitoring progress and ensuring accountability.
Strategies outline the approach taken to reach the Goals. They are the actionable pathways that will bridge the gap between the current state and the Goals set by the organization.
- Measures
Measures provide quantitative or qualitative indicators of success. They are key to evaluating the effectiveness of the Strategies and whether the Goals contribute to achieving the Objective.
Each component of the OGSM Model is mutually reinforcing; the Objective guides the setting of Goals, which in turn inform the Strategies, all of which are quantified by the Measures. The model is used for strategic planning and as a communication tool across an organization to ensure that all members work cohesively towards common aims.
Establishing an Objective
When implementing the OGSM framework, defining the objective is the first and most integral part. This denotes a clear, long-term goal aligned with the organization’s vision and mission and articulates the desired future positioning.
Defining Vision and Mission
The first step is to articulate a Vision. This encapsulates the envisioned future state that an organization aims to achieve. It is a source of inspiration and provides a strategic direction. The Vision sets the ambitious endpoint that everyone within the organization strives to achieve.
Similarly, a Mission Statement defines the organization’s purpose, core values, and reason for existence. The mission guides daily operations and decision-making processes within the organization.
Vision and mission provide a foundation upon which the objective statement is constructed.
- Vision: A compelling image of the future that an organization seeks to achieve.
- Mission Statement: The organization’s core purpose and approach to achieve its vision.
Crafting an Objective Statement
Crafting an Objective Statement requires meticulous articulation of the organization’s intents. An effective objective statement is concrete and measurable, stretching the organization to achieve its long-term goal. It builds upon the vision and mission, translating them into tangible outcomes.
The objective statement answers the question, “What specific accomplishment do we aim to achieve?” and acts as a beacon, directing the formulation of appropriate strategies and actions.
- Objective Statement: Specific, measurable, aspirational, and time-bound description of what the organization aims to accomplish.
To illustrate, if an organization’s vision is to “be the leading innovator in smart home technology,” the objective statement might state, “To capture 25% market share in the smart home devices category by 2028.” The objective must resonate across the organization, providing a clear, focused path to success.
Setting Strategic Goals
When utilizing the OGSM framework, setting strategic goals is a pivotal step. It articulates the desired outcomes and establishes the metrics by which success will be measured.
Identifying Measurable Goals
Measurable goals are the cornerstone of a transparent and accountable strategy. They should be quantifiable and trackable over time, allowing organizations to gauge progress and make informed adjustments.
For instance, setting a revenue goal involves specifying a monetary target within a defined period. Equally, pursuing a market share objective requires precise data on current standings and the desired level of growth to be monitored through continuous market analysis.
- Examples of Measurable Goals:
- Increase revenue by 20% in the fiscal year 2024.
- Attain a dominant presence, capturing 15% of the consumer tech market by the end of Q4.
Aligning Goals with Business Focus
Strategic goals must align with the overarching business focus to ensure coherence and relevance. This alignment involves defining clear objectives that support the company’s broader vision.
For example, if a firm’s focus is customer-centricity, goals may include enhancing customer satisfaction scores or increasing repeat customer rates. These goals should be supported by pertinent Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as the Net Promoter Score (NPS) or customer retention rates, which provide measurable insight into performance against the business’s strategic focus.
- Focused Goal Alignment:
- If focusing on customer satisfaction: Improve NPS by 10 points year-over-year.
- When targeting market expansion: Grow customer base by 25% in new regions.
Developing Strategies
In the OGSM framework, strategy development involves making informed strategic choices and allocating resources effectively to achieve specific objectives. This necessitates a clear understanding of the available tactics and the necessity of prudent budget management.
Strategic Choices and Tactics
When developing strategies, one must consider the range of available strategic choices. This includes evaluating how different tactics can serve the larger goals.
Choices should be based on market research, competitive analysis, and the organization’s internal capabilities. For example, the OGSM model guide emphasizes the importance of strategic clarity in communicating priorities.
- Assess: The assessment of tactical options is critical.
- Select: Selecting the right tactics involves making decisions consistent with the overarching organizational goals.
Resource Allocation
Allocating resources, which include materials, tools, time, personnel, and financing, is a pivotal aspect of strategy execution.
An effective budget must be outlined to ensure resources are properly aligned with the strategic plan.
- Prioritize: Critical initiatives receive the most resources.
- Distribute: The distribution reflects the action plan’s anticipated needs.
Budget considerations and the detailed action plan must align with a realistic appraisal of what is required to implement each chosen tactic. The above-mentioned ultimate guide with examples proves that the balance between resource availability and strategic aims is key for successful implementation.
Measuring Success
In the OGSM Framework, measuring success is a critical step that involves assessing performance against the strategy using various tools and metrics.
Key Performance Indicators
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are quantifiable measures that gauge success and failure in achieving key business objectives. For an organization using the OGSM model, KPIs could include financial targets, customer satisfaction scores, or operational efficiency rates.
Each objective within the OGSM framework should have corresponding KPIs that are:
- Relevant: Directly aligned with the strategic goals.
- Predictive: Indicative of future performance.
- Specific: Clear enough to guide decision-making.
Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard method complements the OGSM model by providing a more holistic view of an organization’s performance. It goes beyond traditional financial metrics, introducing a framework that evaluates an organization across four perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Business Processes, and Learning and Growth.
A Balanced Scorecard might include:
- Financial Metrics: Revenue growth or cost reduction targets.
- Customer Metrics: Market share, customer retention rates.
- Internal Business Process Metrics: Time to market, quality indicators.
- Learning and Growth Metrics: Employee training hours, innovation rates.
Monitoring and Surveys
Effective monitoring involves routine tracking and analysis of measures and metrics to ensure that strategic initiatives are on course.
Conversely, surveys provide qualitative insights from customers, employees, or stakeholders that can inform strategy adjustments.
Regularly scheduled performance reviews and customer feedback surveys are essential tools for:
- Validation: Confirming that the strategies employed are leading to desired outcomes.
- Adaptation: Making necessary changes in response to feedback or shifting market conditions.
- Implementing OGSM
Implementing the OGSM model involves a systematic approach that clearly lays out action plans and sets specific milestones within an agile framework. The process demands a precise alignment of organizational actions with strategic objectives.
Action Plans and Milestones
For effective implementation, one must first create detailed action plans that outline the specific steps needed to achieve the strategic objectives.
These actions should be broken down into smaller, manageable tasks, prioritized, and assigned to appropriate team members. Utilizing software platforms that facilitate project management can ensure these tasks are monitored and controlled efficiently.
A crucial part of the action plan is establishing clear milestones. Milestones are signposts that mark significant points along the project timeline, helping teams measure progress and stay focused on outcomes.
They should be:
- Specific: Clearly define what is to be achieved.
- Measurable: Quantify or suggest an indicator of progress.
- Achievable: Set within the ability to be accomplished.
- Time-bound: Associated with a specific time frame.
| Milestone | Description | Due Date | Owner |
| 1. Launch the initial campaign | Begin marketing push for product X | April 2024 | Marketing Team |
| 2. Evaluate market response | Assess campaign impact on sales | July 2024 | Sales Department |
| 3. Adjust strategic plan | Modify the campaign based on feedback | August 2024 | Leadership Team |
Agile Implementation
Agile implementation of OGSM ensures that the plan remains flexible and responsive to change. This is where the traditional rigidity of strategic planning meets the dynamic flux of the business environment.
Agile methodologies support iterative development. They include regular evaluation and adaptation of strategies. This approach encourages:
- Iterative progress with sprints leads to incremental improvement.
- Frequent review meetings to assess goals and refine strategies.
- A commitment to adaptability allows the organization to pivot in response to new information or market changes.
The nimble structure ensures that the enterprise remains adept at promptly addressing unexpected hurdles or seizing emerging prospects even as overarching goals steer the course. It promotes continuous learning and evolution within the strategic planning process.
Leveraging OGSM Software
OGSM Software presents a transformative strategic planning and monitoring approach in the digital age. It is an indispensable asset for companies striving to optimize the implementation of their strategies.
The software facilitates a structured environment where companies can craft their Objectives, Goals, Strategies, and Measures within a singular platform.
One of the primary advantages of leveraging OGSM Software is its optimization of the planning process.
Businesses can articulate their vision effectively and align collective efforts toward achieving shared objectives. Features that condense complex strategies into accessible, one-page documents give teams clarity and direction, minimizing unnecessary complexity in the planning stages.
- Comprehensive Dashboard: Visual representations of strategies and progress.
- Real-time Updates: Keeps all members informed about the current status and changes.
- Collaborative Workspace: Encourages collective input and transparency.
With OGSM Software, monitoring becomes coherent and less labor-intensive. The tools often include dashboards that provide real-time updates, allowing teams to track progress toward goals efficiently and effectively.
This ensures that organizations can react promptly to deviations from the plan and make necessary adjustments to stay on course.
The software frequently includes built-in analytics and reporting functions, facilitating managers’ examination of performance metrics. It aids in recognizing success patterns or identifying areas that require more attention.
Incorporating OGSM Software into the operational structure empowers businesses with the tools to enact their strategies, nurturing an environment of perpetual enhancement and mastery in strategic execution.
Case Studies
Case studies provide practical examples of companies employing the OGSM framework to navigate complex business challenges. They showcase specific strategies that align daily operations with long-term goals.
Coca-Cola’s Market Strategy
With its vast global presence, Coca-Cola leveraged the OGSM model to refine its market strategy, concentrating on revenue growth through innovative marketing.
The corporation established a precise goal to amplify its market presence, encompassing strategies to boost customer interaction and unveil novel offerings designed to resonate with regional preferences.
Implementing targeted strategies like tailored advertising campaigns and collaborating with regional distributors were key to their success. Their measures included assessing market penetration and revenue metrics to ascertain the strategies’ effectiveness.
Honda’s Innovation Approach
Honda has a long-standing reputation for innovation, particularly in the automotive and technology sectors.
Utilizing the OGSM framework, Honda charted a path toward pioneering new products and technologies.
The company’s objective was to establish itself as a leader in eco-friendly transportation. Strategic goals included developing cutting-edge, fuel-efficient vehicles and creating a more sustainable manufacturing process.
Honda’s strategies capitalized on its strong research and development capabilities, market adoption rates, and reduced environmental impact measured success.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Implementing the OGSM Framework can encounter specific hurdles. Organizations can use this strategic planning tool effectively by recognizing common challenges and their solutions.
Flexibility and Granularity
Lack of Flexibility: While the OGSM Framework helps streamline goals and strategies, its structured nature can sometimes stifle flexibility.
Organizations find that adapting to changes in the market or industry can be cumbersome when tightly bound to predetermined goals and strategies.
Solution: To combat this, they ensure ongoing reviews and allow for iterations of their OGSM. Establishing clear guidelines for when and how to revise the OGSM can maintain strategic direction while allowing for necessary adjustments.
Lack of Granularity: Another challenge is that the high-level overview provided by the OGSM model may overlook the finer details required for execution.
Solution: Organizations counteract this by supporting the OGSM with detailed action plans that capture granularity, breaking down strategies into specific tasks, and assigning clear responsibility.
Top-Down Approach Implications
Impersonal Top-Down Approach: The common top-down implementation of the OGSM Framework often leads to disengagement at lower organizational levels, as employees may feel disconnected from the strategy development process.
Solution: To remedy this, companies involve a wider range of employees in the initial formulation of the OGSM.
They conduct workshops and feedback sessions, which help create a sense of ownership and alignment with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Strategic Planning: A top-down approach may sometimes miss valuable on-ground insights crucial for effective strategic planning and execution.
Solution: Leaders address this by ensuring a two-way flow of communication and incorporating feedback mechanisms.
They encourage department heads and team leaders to provide regular input, effectively integrating various perspectives into the strategic planning process.
Advancing through OGSM
The OGSM framework has emerged as a key player in strategic planning methodologies. It has strategically evolved from earlier concepts to integrate with modern goal-setting frameworks, enhancing the pursuit of long-term visions with precision and clarity.
Evolution from MBO to OGSM
The OGSM framework bears its roots in Management by Objectives (MBO), a concept popularized by Peter Drucker in the 1950s.
MBO served as a foundational approach, emphasizing the importance of clear objectives in management. This structured approach underlined that setting and communicating clear objectives was key to improving organizational performance.
However, with the evolution towards comprehensive strategic planning, OGSM has expanded upon these principles by including specific strategies and measures to achieve set objectives.
Integrating OKR and SMART Goals
Integrating OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) and SMART Goals within the OGSM model strengthens an organization’s ability to execute its long-term strategy.
OKRs emphasize ambitious goal setting connected to measurable outcomes, while SMART Goals stipulate that objectives must be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
By synthesizing these goal-setting methodologies, OGSM presents a refined structure:
- Objectives reflect an organization’s long-term vision and desired future state.
- Goals are quantifiable and leveraged as benchmarks for success, aligning with the SMART criteria.
- Strategies describe the approaches to be employed in pursuit of the objectives.
- Measures are key results and indicators that track the progress of strategies and goals.
Conclusion
The OGSM Model has established itself as a powerful tool in the realm of strategic planning. Utilized by various organizations, including Fortune 500 companies, it stands out for converting abstract visions into concrete plans.
This methodology offers clarity through its articulated components: Objective, Goals, Strategies, and Measures.
Each element of the OGSM Framework serves a specific purpose:
- Objective: The objective is the foundation for the model, outlining the organization’s clear, long-term vision.
- Goals: These are quantifiable benchmarks that progress the organization toward its Objective.
- Strategies: They detail the company’s approach to achieve the Goals.
- Measures: This involves the metrics used to track the success of the Strategies.
The OGSM Framework’s appeal lies in its simplicity and effectiveness. It breaks down complex strategies into actionable elements, aligning them with measurable outcomes. This guarantees that every echelon within the organization comprehends and collaborates towards a unified goal.
The model promotes strategic alignment and facilitates better communication across various departments. Companies leveraging the OGSM Framework can adapt swiftly to market changes while focusing on their long-term objectives, thus upholding their competitive edge.