The SATIR Change Model is a robust framework for understanding the process of transformation and personal growth. Developed by Virginia Satir, a renowned family therapist, this model has transitioned from its roots in family systems therapy to a broad application across various domains, including organizational change and personal development.
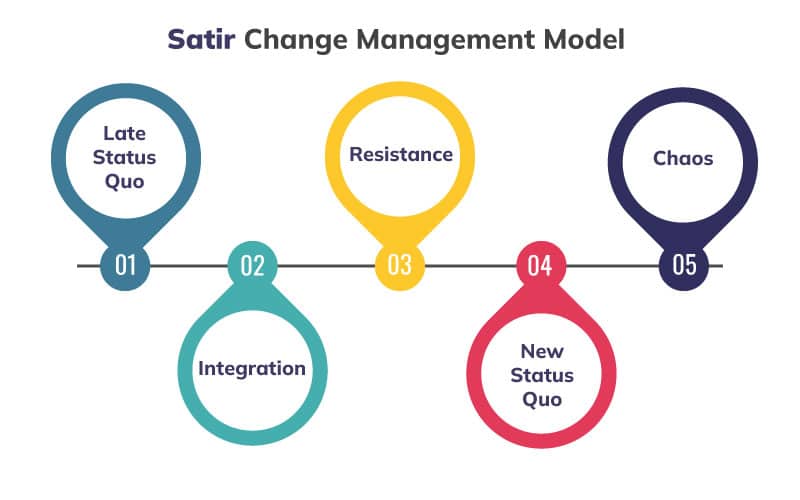
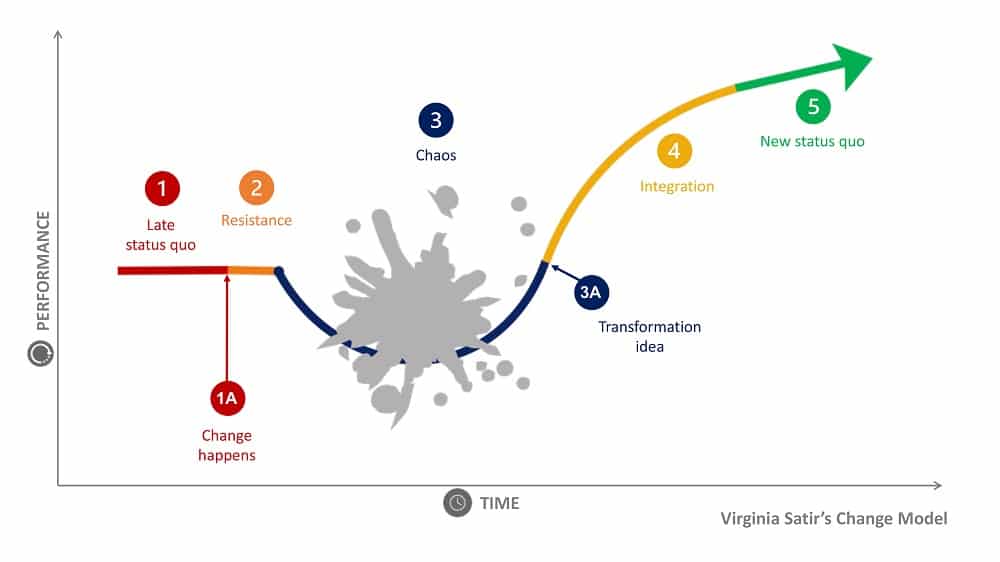
The model outlines five distinct stages of change: Late Status Quo, Resistance, Chaos, Integration, and New Status Quo. It offers insight into the complex human experience during transitions.
Virginia Satir‘s insights into change processes emphasize the importance of the human element. Her model provides a lens through which one can view the emotional and psychological landscapes people traverse during change. Organizations and individuals alike can use the SATIR Change Model to navigate the highs and lows associated with change, understanding that each stage is critical in the journey toward a new status quo.
Applying the SATIR Change Model can facilitate a smoother transition through change challenges. It encourages awareness of the inherent stages and equips those involved with strategies to cope with, adapt to, and ultimately integrate change into their behaviors and practices. This, in turn, fosters resilience and a more profound capability to thrive in new and evolving environments.
Overview of the SATIR Change Model
The SATIR Change Model, originally developed by Virginia Satir, stands as a seminal framework in the field of change management and organizational change. Applying principles derived from family therapy aids in understanding and navigating the complexities of the change process within organizations.
Background and Development
Virginia Satir, a distinguished figure in family therapy, crafted the SATIR Change Model to expedite growth and improvement within the familial unit. This model traverses beyond therapy, offering significant insight into change management. Its underlying philosophy contends that human experiences are a sequence of distinct stages, each of which can be optimized to foster a conducive environment for change.
Application and Scope
Organizations implement the SATIR Change Model as a blueprint for managing transformation initiatives. It encapsulates the nuances of human behaviors during periods of change, enabling leaders to steer their teams through transitions with empathy and effective communication. Its utility is not limited to large-scale organizational change; it also benefits individuals and smaller groups adapting to new circumstances.
The model is celebrated for its versatility and effectiveness across various settings, illustrating that the principles of family therapy can be expertly applied to the dynamics of organizational change.
The Five Stages
The Satir Change Model maps out a transformational process through five distinct and sequential stages that people and organizations undergo during change. Each stage represents a different emotional and psychological state, crucial for navigating and managing change effectively.
Late Status Quo
Stability is the norm in the Late Status Quo, with established behaviors and performance levels. A sense of normalcy and predictability characterizes this stage. However, complacency is also a state that often precedes the catalyst for change.
Resistance and Chaos
Following any disruption of the status quo, Resistance is a natural reaction where individuals or organizations may experience denial, fear, or anxiety. As the reality of change sets in, Chaos ensues, marked by confusion and uncertainty. Performance may decline as old ways are questioned, and new solutions are not found.
Integration and Practice
Integration begins when individuals or groups start to experiment with new behaviors, leading to a critical learning phase. Practice during this stage is essential, as it involves finding what works and adjusting to new approaches, which requires time and patience for refinement.
New Status Quo and Improvement
The final stage, New Status Quo and Improvement is achieved when the change has been fully integrated. This phase is recognized by a renewed sense of stability, improved performance, and a return to high functionality, reflecting the successful adoption and benefit of the change.
Emotional Responses to Change
In the context of the SATIR change model, individuals typically experience various emotions when confronted with change. These emotions are essential to address as they can dramatically influence the success of transition processes.
Dealing with Uncertainty
Uncertainty often triggers a profound emotional response during change. Individuals may feel lost or doubtful about the future, decreasing productivity and morale.
In the SATIR model, acknowledging these feelings is imperative to successfully navigate through the Chaos stage, where uncertainty peaks. Establishing a climate of transparent communication and offering reassurance whenever feasible is imperative for organizations.
Managing Fear and Anxiety
Fear and anxiety are naturally occurring emotions when facing the unknown elements of change. The SATIR change model asserts that recognizing and addressing these emotions is crucial.
For example, denial and anger can be early emotional responses during the Resistance stage before progressing to Exploration, where fear may give way to cautious optimism.
Methods to manage these emotions include providing clear, consistent information and emotional support, ensuring that individuals do not feel isolated during the transition.
Implementing the SATIR Model in Organizations
Organizations adopting the Satir Model benefit from structured progression through change. This requires active managerial involvement, deliberate communication strategies, and robust systems for support.
Roles of Managers and Change Leaders
Managers and change leaders play a pivotal role in steering an organization through the stages of the Satir Model. They recognize the Late Status Quo and initiate the first push towards change.
Their duties include creating an environment that welcomes new ideas and addresses the Resistance phase empathetically. During the Chaos stage, they must remain steady, providing guidance and clarity to prevent drift.
As the organization enters the Integration phase, managers and change leaders must reinforce positive behaviors and solidify gains. This sets the stage for the New Status Quo, where the desired changes are embedded into the organization’s culture.
Effective Communication Strategies
Communication during change must be clear, frequent, and bidirectional. Organizations should emphasize the importance of open communication by creating feedback loops that allow for an honest exchange of ideas and concerns.
Managers can reduce anxiety and build trust by clearly outlining the reasons for change and the expected outcomes.
During the Chaos to Integration stages of the Satir Model, managers need to ensure that communication channels are open and that messages are tailored to address employees’ concerns and motivations.
Supporting Systems and Structures
For the Satir Model to be effective in organizations, systems, and structures must be in place to support the change process.
This includes providing resources such as training and time to adapt to new roles and tasks. It may also involve establishing a dedicated change management team to offer guidance and support during each transition phase.
Organizations should ensure structures are flexible enough to accommodate the experimentation that comes with the Integration phase. This allows for the adaptation and refinement of new methods and processes.
Challenges and Solutions
When exploring the Satir Change Model, one must consider both the hurdles that typically arise and the viable remedies. The implementation phase is often resisted but can be navigated through strategic approaches.
Common Obstacles in Change Management
Organizations frequently encounter a variety of hurdles during change management. Here are some common challenges:
- Resistance from Employees: Staff may resist change due to uncertainty or fear of the unknown.
- Lack of Support: Without sufficient backing from management, change initiatives can falter.
- Inadequate Communication: Change can create confusion if not communicated effectively.
To address these issues, involving employees at every step is essential, ensuring they feel valued and heard.
Strategies for Overcoming Resistance
Here are strategic solutions to counteract resistance:
- Foster Support: Engage leadership to champion the change, providing a stable foundation for transformation.
- Enhance Communication:
- Deliver clear, consistent messages.
- Offer a platform for open dialogue.
- Create Feedback Channels: Implement mechanisms to collect employee feedback, acknowledging their input and concerns.
- Empathy: Show understanding of employee sentiments to create a supportive atmosphere during transitions.
Measuring Success and Productivity
In the context of the Satir Change Model, gauging success and productivity involves both the assessment of current performance and the ongoing enhancements to sustain growth. Successful monitoring and evaluation set the stage for continuous improvement and long-term transformation benefits.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Monitoring is the systematic collection of data related to the performance of an organization going through change. It is a critical component of the Satir Model as it allows stakeholders to track whether the change is progressing as intended.
Indicators of success and productivity here can include:
- Performance Metrics: Quantitative data such as output rates, sales figures, and customer satisfaction.
- Employee Feedback: Qualitative insights from those experiencing the change firsthand.
Within this framework, evaluation is the interpretation of monitoring data to assess the impact of the change. It confirms whether the anticipated benefits are being realized or if corrective measures are necessary.
This cyclical process ensures that the organization remains aligned with its objectives during a transition.
Continuous Improvement and Transformation
The essence of continuous improvement within the Satir Model lies in iterative learning and development. It recognizes that change is not a one-time event but a constant endeavor where:
- Every iteration of the process is an opportunity to enhance productivity.
- Performance insights lead to better strategies and more effective implementation.
Transformation unfolds as the cumulative effect of continuous improvement efforts. This is where one sees significant leaps in performance and productivity, indicating that the seeds of change are deeply rooted and are blooming into success.
The journey to this point is marked by incremental benefits that compound to deliver substantial and lasting organizational advancements.
Case Studies and Real-world Applications
The Satir Change Management Model has demonstrated its effectiveness through numerous organizational case studies and personal transformations. These real-world applications showcase the model’s versatility across different contexts, underscoring its value in facilitating transformative change over time.
Organizational Case Studies
- Technology Firm Adoption: A large technology company applied the Satir Model to manage the transition to a new software platform. Employees experienced increased productivity and morale as they moved from chaos to a new status quo, integrating changes within a few months.
- Healthcare System Overhaul: A regional hospital integrated the Satir Model into its operations to navigate a comprehensive policy update. The transformative process was documented, revealing a significant improvement in patient care and staff satisfaction over a two-year period.
Personal Transformations
- Leadership Development: An executive coaching program incorporated the stages of the Satir Model to support individual leaders undergoing transitions. Case studies illustrate personal growth and improved leadership capabilities, often linked to better organizational outcomes.
- Coping with Major Life Changes: Therapists have utilized the Satir Model to guide individuals facing significant life alterations, such as career changes or personal losses. Documented transformations reveal the model’s capacity to help individuals reach a new sense of balance more rapidly and with greater resilience.
Tools and Resources for Applying the SATIR Model
When implementing the Satir Change Model, a number of tools and resources are essential for success.
Training is the cornerstone of effective application. Individuals and organizations can benefit from workshops and seminars that delve into the model’s intricacies and application strategies.
The five stages of the Satir Model—Late Status Quo, Resistance, Chaos, Integration, and New Status Quo—require understanding specific resources.
Diagrams and flowcharts visually represent how an entity moves through the change curve. Similarly, checklists and templates assist in tracking organizational improvements and phases of change.
Implementation tools such as readiness assessments prove invaluable.
These help gauge an organization’s preparedness for change, identifying potential resistance points early in the process. Furthermore, reflective journals or logs can be instrumental during the Integration phase, offering insights into personal and organizational growth.
Interactive technologies, for example, can simulate various scenarios, providing a risk-free environment for testing responses to change.
Online platforms dedicated to the Satir Model serve as repositories of knowledge, often providing case studies, articles, and forums for discussion.
Below is a table summarizing key tools and resources:
| Phase | Tools/Resources |
| Late Status Quo | Readiness assessments, status reports |
| Resistance | Communication plans, feedback mechanisms |
| Chaos | Coaching, stress management techniques |
| Integration | Training sessions, reflective journals |
| New Status Quo | Performance metrics, continuous feedback |
Access to knowledgeable consultants who specialize in the Satir Model can offer tailored guidance for specific organizational contexts.
They can offer personalized training sessions and sustained support throughout the application of the model, ensuring that teams remain aligned with their change objectives.