Understanding the 70-20-10 Model
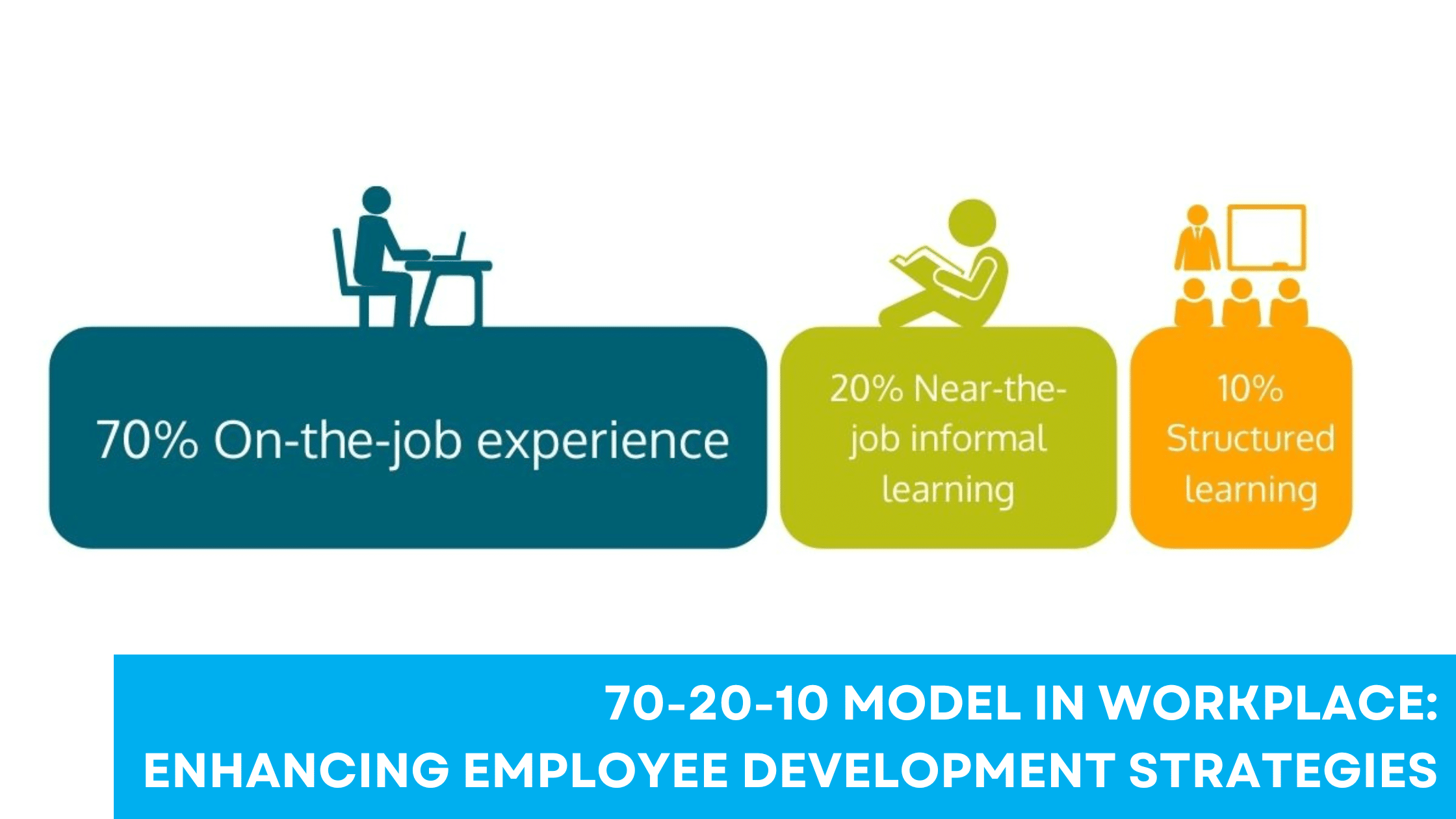
The 70-20-10 model is a framework that guides learning and development in the workplace. It divides learning experiences into on-the-job experiences, social learning, and formal education, each with a specific percentage.
Origins and Development
The 70-20-10 model originates from studies in the 20th century focusing on professional learning. This model was developed based on the understanding that most learning occurs through hands-on experiences.
Key Contributors: Researchers and theorists contributed to shaping this model by observing how adults learn at work. Their studies revealed that a significant portion of skills are acquired through direct experience.
This model has evolved as organizations seek a balanced approach to developing employees. It emphasizes practical learning over traditional classroom settings. This shift reflects the changing dynamics of workplace learning, making it relevant today.
Core Principles
The framework breaks down learning into three main components:
- 70% Experience: This part focuses on practical, on-the-job learning. Employees gain insights through day-to-day tasks and challenges, which enhance their skills and competencies.
- 20% Exposure: Social learning accounts for this portion. It happens through interactions, feedback, and mentoring. Both in-person and online platforms can facilitate this process.
- 10% Education: Formal training and coursework complete the model. This structured learning is essential but supplements the more significant informal experiences.
By integrating these three elements, organizations can design a well-rounded training strategy that addresses diverse learning needs.
Components of the Model
The 70-20-10 model divides learning into three main parts: experiential, social, and formal learning. Each component has a unique role in shaping skills and knowledge in the workplace.
Formal Learning Explained
Formal learning constitutes 10% of the model. It involves structured educational experiences such as training sessions, workshops, and classroom-based learning. These sessions are typically instructor-led and follow a set curriculum or syllabus. They are crucial for providing foundational knowledge and skills that are often necessary before engaging in more practical applications.
Certifications and structured courses also fall under this category. Formal learning offers employees a clear path to achieving specific educational goals. Although it forms the smallest portion in the model, its structured approach ensures standardization and consistency in learning certain key elements.
The Role of Social Learning
Social learning represents 20% of the 70-20-10 model. It takes place through interaction and collaboration among colleagues. This type of learning happens in the workplace via sharing ideas, observing others, and receiving feedback. It leverages the social aspect of work, allowing individuals to learn from each other’s experiences.
Mentorship and peer reviews are examples of social learning. While less structured than formal learning, it is more interactive. This format helps individuals quickly adapt to new situations and roles by learning informally from their peers, making it an effective way to share valuable insights and practical knowledge.
Experiential Learning in Depth
Experiential learning comprises 70% of the model, emphasizing learning through direct experience. This method is based on real-world tasks and challenges that require individuals to apply their skills and knowledge practically. It helps employees learn by doing, encouraging the immediate application of learned concepts.
On-the-job training, internships, and project assignments are forms of experiential learning. This approach is considered the most effective because it enables individuals to face real scenarios. The hands-on nature ensures that learning is directly related to one’s work duties, fostering deeper understanding and retention of skills over time.
Implementing the Model in the Workplace
Implementing the 70-20-10 model involves aligning strategies to improve learning and development. By supporting informal learning and fostering a strong learning culture, organizations can enhance employee growth.
Strategic Alignment
To effectively implement the 70-20-10 model, organizations must align their learning strategies with business goals. This means integrating learning into daily workflows. Leaders should identify specific skills needed for business success and design learning experiences that provide these skills.
Performance metrics can help track progress and align with desired outcomes. For instance, incorporating learning objectives in performance reviews ensures that employees stay focused on developing relevant skills.
Clear communication is crucial to ensure all employees understand the importance of this model. Providing examples and setting success stories can demonstrate the benefits of workplace learning.
Supporting Informal Learning
Informal learning accounts for a significant portion of the 70-20-10 model. Organizations should encourage employees to learn from each other and through real experiences. This includes facilitating mentorship programs where experienced employees guide others.
Creating spaces or times for informal learning, such as breakrooms or lunchtime workshops, can promote knowledge sharing. Digital platforms or internal forums can also serve as venues for employees to discuss challenges and solutions.
Managers should recognize and reward informal learning efforts, reinforcing the value of continuous development. This approach helps employees apply new skills on the job, enhancing overall performance.
Promoting a Learning Culture
A strong learning culture is essential for the 70-20-10 model to thrive. Companies need to create an environment where learning is valued and encouraged. Leadership plays a key role by setting an example and actively participating in development activities.
Providing access to learning resources, online courses, or workshops signals the importance of growth. HR can organize training sessions or group discussions on various topics, ensuring a constant flow of new information.
Cultivating curiosity and openness among employees encourages them to seek knowledge independently. This mindset results in a more agile and adaptable workforce, which is crucial for meeting the changing demands of the workplace today.
Impact on Employee Performance
The 70-20-10 model significantly influences employee performance by enhancing productivity, improving problem-solving skills, and fostering effective training programs. By focusing on experiential and social learning, employees gain practical experience and insights that directly impact their work efficiency and effectiveness.
Enhancing Productivity
The 70-20-10 model dedicates 70% of learning to hands-on experiences, which directly enhances productivity. Employees learn while doing, allowing them to apply new skills immediately. This leads to quicker adaptation to tasks and improvement in task execution. Practical experience helps employees develop confidence in their abilities, reducing hesitation and increasing output.
Additionally, this model supports continuous learning, making employees more adaptable to changes in work processes. This adaptability is crucial in industries where rapid technological advancements demand quick skill updates. Overall, experiential learning encourages a proactive approach, where employees are more engaged and motivated to excel in their roles, thereby improving overall productivity levels.
Improving Problem-Solving Skills
Emphasizing real-world experiences, the 70-20-10 model enhances problem-solving skills. When faced with actual challenges, employees are pushed to think critically and develop solutions. This constant exposure to problem-solving scenarios trains employees to approach issues methodically and with confidence.
Social learning, accounting for 20% of the model, plays a crucial role here. By interacting with peers and mentors, employees gain diverse perspectives on handling problems. Sharing experiences fosters creative solutions and collaborative problem-solving. Organizations benefit from employees who can independently and collectively address issues, ultimately leading to more innovative and efficient business practices.
Building Effective Training Programs
Incorporating the 70-20-10 model into training programs shifts the focus from traditional methods to integrated learning experiences. By aligning 10% of learning with formal training, companies build a foundation of knowledge that supports hands-on and social learning components. These training programs prioritize relevance and practicality, ensuring employees gain applicable skills.
This approach encourages a culture of learning, where new knowledge is constantly incorporated into daily tasks. The model’s integration creates more personalized and effective training routes that cater to individual learning needs, enhancing the capability and performance of each employee. Well-structured programs lead to better retention and application of skills, fostering a competent and dynamic workforce.
Training and Development Strategies
Training and development in the workplace often utilize models like the 70-20-10 framework, which emphasizes a mix of experiential, social, and formal learning. Focusing on tailored strategies enhances employee growth and boosts organizational success.
Leadership Training
Leadership training is crucial for cultivating strong and effective leaders within an organization. It focuses on enhancing skills such as decision-making, communication, and strategic thinking. Programs often include workshops, mentoring, and coaching to build on these skills.
Workshops provide participants with interactive learning opportunities, allowing them to apply new knowledge through practical scenarios. Mentoring pairs less experienced employees with seasoned leaders, fostering a hands-on learning environment. Leaders also benefit from theoretical insights and practical tools to handle real-world challenges effectively, aligning with experiential learning principles.
On-the-Job Training Methods
On-the-job training is an essential component of the 70-20-10 model, where it represents experiential learning, accounting for 70% of learning opportunities. This approach allows employees to gain firsthand experience by working directly on tasks in their job roles.
Methods such as job shadowing and rotational programs enable employees to learn by observing seasoned colleagues and practicing skills in different departments. These strategies help employees adapt swiftly to varying situations, improving their problem-solving abilities and boosting their confidence. Hands-on experience is invaluable in reinforcing knowledge and enhancing skill sets, ensuring that learning is practical and relevant.
Developing Talent Management
Talent management focuses on identifying and nurturing potential leaders and skilled professionals within the organization. A strategic approach involves aligning talent development with organizational goals to maximize employee contributions.
Key strategies include succession planning, where potential leaders are groomed for future roles, and performance management to regularly assess and guide employee progress. Formal training programs also play a role by providing structured learning opportunities. These approaches not only support the growth of individual employees but also bolster overall organizational development. Effective talent management results in a robust workforce ready to meet future challenges seamlessly.
Feedback and Coaching
Feedback and coaching are crucial elements in the 70-20-10 model, enhancing both learning and performance at work. Emphasizing continuous feedback ensures constant growth, while coaching supports goal achievement.
Mentoring and Mentorship
Mentoring involves experienced individuals guiding less experienced ones in their career journey. It differs from regular feedback by focusing on long-term growth and development. Mentors offer valuable insights and share real-world experiences, helping mentees navigate challenges.
A strong mentorship relationship can lead to significant skill development. It fosters a sense of confidence and encourages individuals to take ownership of their learning. This approach leads to more dynamic personal development and prepares employees for future roles.
Continuous Feedback Loops
Continuous feedback loops are essential for effective learning. They involve regular evaluations and adjustments to improve performance. This ongoing feedback reduces the gap between expectations and actual performance, focusing on areas needing improvement.
Frequent feedback allows individuals to fine-tune their skills. It enhances responsiveness to changes and ensures that employees meet their goals. Teams that adopt this method are typically more agile and adaptable, ready to tackle new challenges.
The Role of Coaching in Learning
Coaching in the workplace is a targeted process, often conducted one-on-one. Coaches help individuals set and achieve specific goals, often related to job performance. They guide employees to overcome obstacles and hone specific skills.
Effective coaches ask powerful questions, encouraging self-reflection and self-discovery. By facilitating a deeper personal connection to learning, coaching empowers employees to take the initiative. This role is vital in helping employees become more proactive and self-sufficient, enhancing their contribution to the organization.
Leveraging Technology in Learning
Integrating technology into workplace learning programs can significantly enhance effectiveness and engagement. Key strategies include utilizing e-learning platforms, embracing mobile learning solutions, and incorporating webinars for diverse learning experiences.
Elearning and Digital Platforms
Elearning platforms provide a flexible and wide-reaching approach to professional development.
These platforms allow employees to access a vast array of learning materials online tailored to their specific roles and skill levels.
Companies can use learning management systems (LMS) to track learning progress and outcomes.
Digital resources such as video tutorials, interactive modules, and quizzes make learning more engaging.
Furthermore, leveraging these platforms supports remote collaboration and enables employees to learn at their own pace.
This approach not only reduces the time needed for learning but also cuts down costs associated with traditional classroom settings.
The Emergence of Mobile Learning
Mobile learning has emerged as a significant trend in educational technology, offering learners access to information anytime and anywhere.
This method fits seamlessly into busy work schedules, allowing employees to learn on the go.
Apps and mobile-friendly websites make it easier to access courses and learning materials right from their smartphones or tablets.
This on-demand learning solution is highly beneficial for field workers or those with non-traditional work shifts.
Furthermore, mobile learning supports interactive content such as podcasts, videos, and games that enhance engagement.
Companies can leverage these capabilities to boost the uptake and completion rates of their learning programs.
Webinars as a Learning Tool
Webinars are a valuable tool for delivering educational content to large audiences in real time, with the added benefit of being cost-effective.
They allow subject matter experts to present topics interactively, often integrating live Q&A sessions with participants.
Companies can easily record these sessions for later use, creating a library of resources for ongoing learning.
Webinars facilitate social learning by enabling interaction among participants, fostering a sense of community and collaboration.
This aligns with the 70-20-10 learning model, which emphasizes the importance of social learning in professional development.
Learning through Collaboration and Engagement
Learning in the workplace thrives when employees engage in collaborative environments. This approach not only enhances learning experiences but also boosts employee engagement.
Fostering Collaborative Environments
Creating spaces where employees feel comfortable collaborating is crucial for effective learning.
When team members work together, they share knowledge, skills, and ideas, which enriches individual understanding and problem-solving abilities.
To foster this environment, organizations can implement regular team meetings, brainstorming sessions, and cross-department projects.
Tools like:
- Video conferencing
- Project management software
- Collaborative platforms
These facilitate seamless communication and streamline teamwork.
Encouraging open communication and building trust among team members is essential.
Recognizing and valuing diverse perspectives further strengthens the collaborative spirit.
By promoting a culture of collaboration, organizations create a learning-rich environment.
Employee Engagement Strategies
Employee engagement is vital for enhancing learning in the workplace. When employees are engaged, they are more motivated to contribute to collaborative efforts and absorb new information.
Strategies include:
- Providing personalized training sessions
- Setting clear goals and feedback loops
- Encouraging peer mentoring
These methods help employees feel valued and connected to their work.
Implementing engagement strategies ensures that learning becomes a continuous and interactive process.
By aligning employees’ interests with organizational goals, companies can maintain high levels of motivation and effective learning outcomes.
Organizational Culture and Growth
Creating a positive organizational culture and focusing on growth through learning are key elements for success. By fostering an adaptive culture, businesses can better meet evolving challenges while promoting continuous development.
Building an Adaptive Culture
An adaptive culture is crucial for organizations to thrive in a changing environment.
It promotes flexibility, encouraging employees to think creatively and embrace new ideas.
Leadership plays a vital role in shaping this culture by showing openness to change and guiding their teams through transitions.
Policies and practices should support innovation and risk-taking, ensuring team members feel safe to offer fresh solutions.
Regular feedback and open communication are essential in maintaining an adaptive culture.
Employees need spaces to voice concerns and suggest improvements.
This dialogue helps identify organizational needs and adjust strategies accordingly.
Recognizing achievements and facilitating collaboration further strengthens the culture, making the organization more resilient and ready to adapt.
Growth through Learning
A strong learning culture is fundamental for organizational growth. By prioritizing development, companies equip employees with the necessary skills and knowledge.
This model often includes a combination of experiential, social, and formal learning.
For instance, Unilever’s approach illustrates how the 70-20-10 model can foster a thriving culture of learning and growth.
Experiential learning involves on-the-job experiences, allowing employees to learn by doing.
Social learning encourages peer interactions, mentoring, and discussions, while formal learning includes structured training and courses.
This comprehensive approach ensures continuous skill enhancement, driving both personal and organizational growth.
Emphasizing learning as a core value not only boosts performance but also helps retain talent by demonstrating a commitment to employee development.
Personalization and Learning Preferences
Personalization in learning focuses on catering to individual learning styles and preferences. This approach enhances personal development, making learning more effective for employees by aligning content with their unique needs.
Catering to Different Learning Styles
Learning styles vary, including visual, auditory, and kinesthetic preferences.
Organizations can optimize training by recognizing these differences.
Visual learners benefit from diagrams and charts, while auditory learners need discussions and spoken instructions. Kinesthetic learners thrive on hands-on activities.
Personalized training materials consider these preferences.
Incorporating multimedia content, interactive modules, and group discussions can address diverse learning needs.
By customizing learning experiences, companies can increase engagement and improve retention rates, leading to more successful personal development.
Adaptive Learning Solutions
Adaptive learning solutions adjust the learning pathway based on individual progress and performance.
These solutions use technology to provide real-time feedback, helping learners focus on areas needing improvement.
This approach allows employees to learn at their own pace, fostering a deeper understanding of the material.
Data-driven analytics play a crucial role in adaptive learning.
By analyzing user interactions, adaptive systems tailor content to fit individual skill levels and preferences.
Employees are then empowered to take charge of their learning journey, aligning personal development with corporate goals.
This personalization increases efficiency and motivation, supporting broader learning and development initiatives in the workplace.
Measurement and Enhancement of Learning
Measuring and improving learning in the workplace involves examining how effective training methods are and utilizing tools that provide valuable insights. This ensures that employees are acquiring the skills necessary for enhanced performance.
Assessing the Effectiveness of Training
To determine if training is effective, it’s crucial to track performance before and after learning sessions.
By comparing task completion rates and quality, organizations can assess skill improvement.
Feedback from employees provides insights into the relevance of training content and delivery. Surveys and focus groups are common methods to gather this information.
Data on retention rates of employees and their advancement within the company can also serve as indicators of effective training.
A good program should lead to both personal growth and organizational development.
Tools for Learning Analytics
Organizations utilize various tools to enhance learning analytics.
Learning Management Systems (LMS) are pivotal as they track progress and customize learning paths.
Data visualization tools present analytics in a comprehensible way, aiding in interpreting employee progress over time. This helps in identifying areas that need improvement.
Another important tool is feedback software to gather continuous input from employees about their learning experiences.
These tools offer insights into what training strategies are working.
Continuous Learning and Evolution
The 70-20-10 model emphasizes acquiring skills through experience and social interactions. This approach encourages lifelong learning and adapts to challenges in professional settings, ensuring continuous growth and development.
Promoting Lifelong Learning
Continuous learning is essential in today’s fast-paced work environment.
The 70-20-10 model supports lifelong learning by integrating education directly into daily tasks.
This method encourages employees to learn from their experiences and engage with colleagues to solve problems.
Reflection plays a crucial role in this process.
By regularly assessing their work and interactions, individuals can identify areas for improvement and growth.
This model also fosters a culture where seeking new knowledge becomes part of everyday work life, thus promoting continuous professional development.
Adapting to Real-World Challenges
In a dynamic workplace, adapting to real-world challenges is crucial.
The 70-20-10 model prepares employees by emphasizing practical experience.
Employees face problems that require immediate solutions which develop their ability to respond to challenges effectively.
This model encourages reflection, allowing individuals to learn from past experiences and apply new insights.
By fostering adaptation skills, organizations can enhance their workforce’s ability to handle change, making them more resilient and capable in diverse situations.
This approach ensures that learning is both relevant and immediately applicable in professional settings.
Conclusion
The 70-20-10 model offers a structured approach to workplace learning. It suggests that 70% of knowledge comes from practical experiences, 20% from interactions with peers, and 10% from formal educational settings.
Organizations adopting this model often witness improved performance and engagement. By integrating learning directly into workflows, employees tend to acquire skills more organically.
Benefits of the 70-20-10 Model:
- Enhanced Learning: Employees learn more effectively through hands-on experiences.
- Collaboration: Encourages peer-to-peer learning and mentoring.
- Resource Allocation: Focuses resources on integrating learning into daily tasks.
For managers and team leaders, this model highlights the importance of creating opportunities for experiential learning. It also underlines the role of feedback and collaboration in skill development.
Shifting the focus from traditional classroom-based training to integrating learning into everyday work activities can lead to better outcomes. Understanding and implementing this approach can provide lasting benefits for both individuals and organizations.